The term “cloud computing” refers to the Internet-based provision of computing services. These services could include things like servers, software, databases, or storage. Users frequently rent them from a provider for a regular monthly fee.
Cloud providers offer computation online in a similar way that you might pay Netflix to distribute television material over the Internet.
Cloud computing gives significantly more flexibility than conventional “build your own infrastructure” models and is quicker and simpler to set up.
How does Cloud Computing work?
Cloud computing works by giving users access to a network of remote servers and computing resources over the internet.
In most cases, a third-party cloud computing provider manages and maintains these servers, and it is their job to make sure the infrastructure is secure, reliable, and available to customers.
It’s a convenient and economical way to utilize computing facilities via the Internet without the expense of purchasing and operating the necessary IT systems.
- Cloud computing resources are managed by a third-party provider, who sets up and maintains the infrastructure.
- Users can use a variety of devices, including laptops, tablets, and smartphones, to access cloud computing resources over the internet.
- The cloud provider offers a wide range of computing resources such as storage, processing power, and software programs, that customers can access as needed.
- When a user requests a cloud computing service, the cloud provider’s computers process the request and assign the required resources to handle it.
- Cloud service providers usually provide a variety of security and data protection features to help secure customer data and prevent illegal access.
What Is Cloud Storage?

Services that are made available across a network are referred to as the cloud. Data backup, management, and access are all done remotely via cloud storage, typically over the Internet. Users often pay a monthly fee per gigabyte for their cloud data storage.
Therefore, the cost of maintaining your data on the cloud will increase as your data volume increases and vice versa.
There are three primary types of cloud storage architecture, public, private, and hybrid.
Public cloud
Services for public cloud storage provide a multi-tenant hosting infrastructure that serves well for unstructured data.
Private cloud
Users that require flexibility and control over their data can choose private cloud storage, which offers a specialized environment protected behind a company’s firewall.
Hybrid cloud
A hybrid cloud gives enterprises the flexibility and more alternatives for deploying their data by combining private cloud and public cloud services.
Also Read Cybersecurity Demystified: Unlock the Incredible Secrets to Protect Your Digital World!
Cloud Computing Services Models
SaaS

‘Software as a service’ is referred to as SaaS. It is a facility that offers users pay-per-use application software on demand. Unlike software that has been purchased under the license, you don’t need to install any software on your PC to use this service because it works across all platforms. Multiple users can access the software through the cloud, which runs a single instance of it. Cloud computing is hence affordable. The vendor is alone in charge of managing the computing resources necessary to provide SaaS. A web browser or small client programs can be used to access this service.
PaaS

PaaS stands for Platform-as-a-Service. This service is essentially a development environment and includes an operating system, a web server, a database, and an environment for running programming languages. All of this comprises the atmosphere in which users can create, compile, and run their applications without being concerned about the underlying infrastructure.
You control the application resources and the data in this model. All other resources are to be managed by the vendor.
IaaS
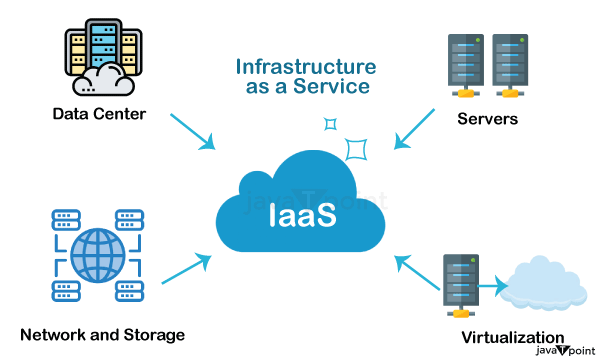
The abbreviation “IaaS” refers to “Infrastructure as a Service”. This service provides all computer resources in a virtual environment so that numerous users can use them. It also provides computing architecture and infrastructure. Data storage, virtualization, servers, and networking are some of these resources. The majority of vendors are in charge of overseeing the stated resources.
You will be in charge of managing additional resources, including apps, data, runtime, and middleware if you want to use this service.
Cloud Security
Protecting cloud-based data applications and infrastructure against online threats is known as cloud security. More and more crucial apps and data are moving to the cloud as cloud usage increases. Although most major cloud service providers, or CSPs, provide conventional cybersecurity measures, they occasionally don’t give enough protection for what the company needs, which increases the risk of data loss and theft.
The CSP is often in charge of the facilities and software networking that run the cloud, but not the security, including how the CSP resources are set up and used. Cloud security services aim to cover these holes in the shared responsibility model; nonetheless, the customer and CSP vendors must agree on who is in charge of what security measures.
Cloud Security Tools
CWPPS(Cloud workload protection platforms)
CASB(Cloud access security brokers)
CSPM(Cloud security posture management)
SASE(Secure access service edge)
ZTNA(Zero trust network access)
To ensure risk-free and secure cloud operations, a cloud security policy is essential. The procedures needed to safeguard cloud data differ depending on the sensitivity and kind of the data, the cloud architecture, the quantity and type of authorized users to gain access to the data, and more. However, some general best practices for protecting cloud data include encrypting data while it is in transit and at rest. Verify the user’s identity with multi-factor authentication. Install firewalls, intrusion prevention and detection tools, and anti-malware software.
To guard against ransomware threats, isolate cloud data backups. and make sure the data is under control, and that you keep track of every data access and additional modifications.
Pros and Cons of Cloud Computing
Pros
- No more external storage devices.
- You can access your cloud account and update your files from anywhere in the world.
- Sharing files has been made super easy.
- Offers one of the best encryption possible i.e. zero-knowledge encryption through which only you can ever access the data.
Cons
- You can’t access the data on the cloud without a network connection. Syncing your files can help avoid this but, if someone else modifies a file while you’re offline, you won’t be able to see the changes made until you get back online.
- Like most online services cloud computing charges you for your storage. Now, if you only need 10 -15GB of storage, you’ll be satisfied with a free service, but you’ll be charged for anything more than that.
- Be careful while choosing a service, when people see a service offering loads of storage for free they just save all their data onto that service. These types of services are usually scams that take your data and sell it.
Uses of Cloud Computing
There are many possible applications and benefits of cloud computing for people, companies, and organizations, and they are constantly developing as new use cases and apps are created.
Common applications for cloud computing include:
Data storage and backup
Data can be stored and backed up using cloud storage services, enabling users to access their files from any device with an internet connection.
Software as a service (SaaS)
Instead of installing programs and software locally on a computer, users can access them online using cloud-based software services like Microsoft Office 365 or Google Workspace.
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
Cloud computing can be used to provide infrastructure services, such as virtual machines or servers, that can be used to create and host applications and websites.
Big data analytics
Large datasets may be stored, processed, and analyzed using cloud computing, which enables businesses and organizations to gather facts and make data-driven decisions.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Cloud computing can be used to manage and interpret data gathered by connected devices, for instance smart appliances.
Collaboration and Communication
Cloud-based collaboration tools, such as Microsoft Teams or Slack, can be used to enable remote communication and collaboration among teams and organizations.
Future of cloud computing
Given how quickly the technology is growing and evolving at a rapid pace, the future of cloud computing appears promising.
As more organizations and individuals rely on the cloud to satisfy their computing needs. Here are some potential developments that could occur in the upcoming years:
- Greater adoption of hybrid cloud solutions, which will let businesses use both public and private cloud infrastructure based on their specific requirements.
- As edge computing continues to expand, performance is enhanced and latency is decreased by processing data closer to where it is generated or utilized.
- The growing popularity of AI and machine learning in cloud computing applications, which can be used to automate tasks and enhance decision-making.
- The development of more specialized cloud services, such as industry-specific solutions intended to meet the unique requirements of different sectors.
- Further security and data protection upgrades, including the use of blockchain technology and other advanced security methods to stop illegal access and data breaches.


